Introduce High Performance Butterfly Valves
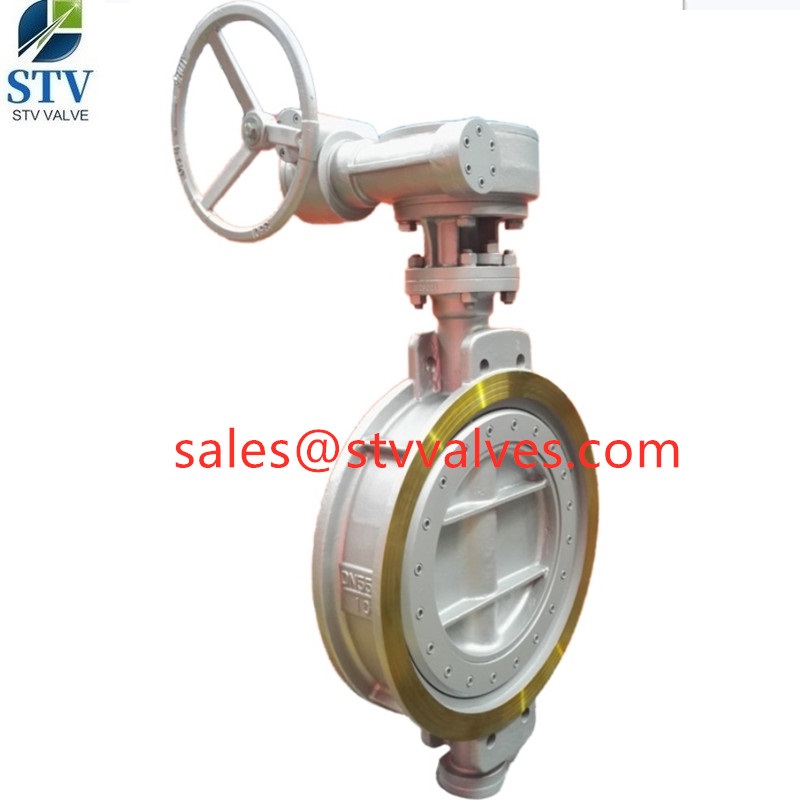

Wafer Butterfly Valve Supplier, Wafer Butterfly Valve Factory
High performance butterfly valves are essential for precise flow control in demanding industrial applications. In this article, we discuss butterfly valves, why they are needed, and compare them to general service valves.
What are Butterfly Valves?
Butterfly valves are a quarter-turn valve, meaning their valve stem only rotates 90° to open or close. This makes them a popular option in applications requiring a fast shutoff. Also, they are common in various industries for their simplicity, compact design, and cost-effectiveness. At larger valve sizes, butterfly valves have a smaller installation footprint and less weight than most valves. Like other industrial valves, butterfly valves consist of a body, actuator/handle, and trim (disc, stem, and seat). However, its unique feature is its disc, which flaps like a butterfly’s wings to allow or stop flow through the valve.
How Do Butterfly Valves Work?
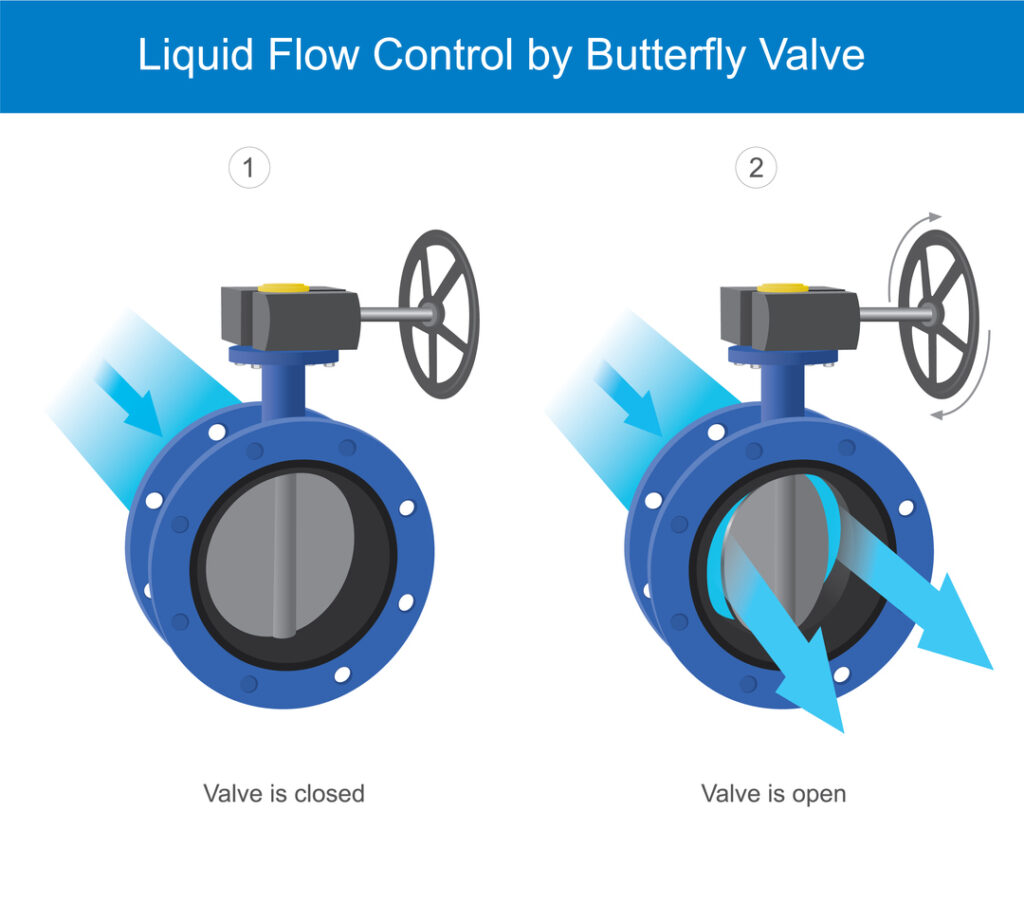
- Open Position: When the handle or actuator rotates the stem, the disc turns to align with the flow, allowing fluid to pass through with minimal resistance.
- Closed Position: When the disc rotates perpendicular to the flow, it blocks the passage, stopping the fluid flow.
High Performance Butterfly Valves
High-performance butterfly valves (HPBVs) are simply butterfly valves with a design that allows them to handle more demanding conditions than general service butterfly valves. They offer several advantages:
- Higher Pressure and Temperature Ratings: HPBVs can operate under higher pressures and temperatures, making them suitable for more rigorous applications. Generally, these valves can operate between -28 °C and 500 °C (-18 °F to 932 °F) and pressures up to 51 bar.
- Better Sealing: They often use advanced sealing technologies, such as metal-to-metal seals, especially at very high temperatures and pressures. Hence, it ensures a tight seal even in challenging conditions. For less onerous conditions, valve sealing could be done using PTFE, EPDM, and NBR.
- Enhanced Durability: The construction materials and design of HPBVs provide greater resistance to wear, corrosion, and other forms of degradation. As a result, high performance valves have a longer service life.
- Improved Flow Control: HPBVs offer better control over fluid flow with less risk of leakage and more precise throttling capabilities.
Types of High Performance Butterfly Valves
High performance butterfly valves come in several designs, each offering specific advantages depending on the application. The following sections highlight some common types.
Double Offset Butterfly Valves
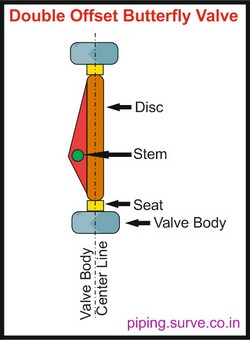
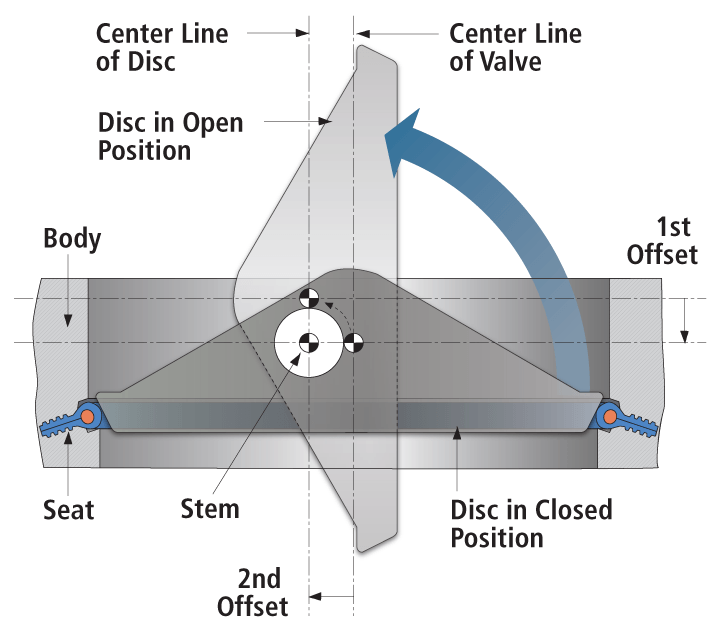
This type of butterfly valve can deliver high performance by having two distinct offsets in its trim configuration. The first offset positions the stem behind the centerline of the sealing surface of the disc, while the second offset positions the stem off-center from the body centerline. As a result, the valve disc only contacts the seat at the final moment of closure, thus minimizing operational torque requirements, friction, and wear. Double offset butterfly valves provide a tight shut-off, which makes them suitable for applications where leakage control is critical.
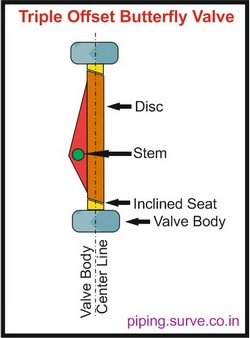
Triple Offset Butterfly Valves
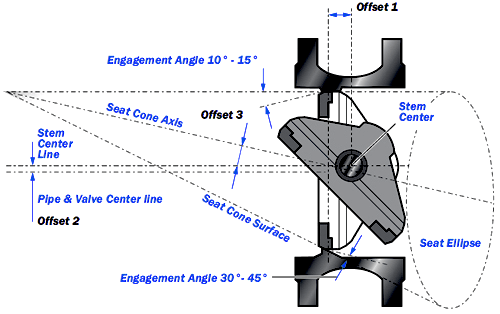
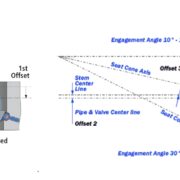
Triple offset butterfly valves have the same offsets as their double offset counterparts but with an additional offset. The third offset introduces a conical profile to the sealing surfaces, which ensures that the contact is perpendicular. This means that the sealing surfaces make no contact until the valve is fully closed, thus eliminating any form of friction and paving the way for metal-to-metal seals. This design provides superior sealing, allowing butterfly valves to serve in high-temperature, high-pressure, and cryogenic conditions.
High Performance Butterfly Valves vs Butterfly Valves
The following table highlights several differences between general service butterfly valves and high performance butterfly valves.
| Feature | General Service Butterfly Valves | High Performance Butterfly Valves |
| Design | Generally have a concentric design with the stem centered in the valve body and the disc | Often feature an offset design to reduce friction and improve sealing |
| Sealing Mechanism | Uses a soft seat made of materials like rubber or elastomers | Utilizes a metal-to-metal seat or a combination of metal and resilient materials |
| Druckrate | Suitable for low to moderate pressure applications as well as temperatures up to 200°F (93°C) | Designed for high pressure and high temperature applications, including cryogenic conditions |
| Cost | Generally lower cost due to simpler design and materials | Higher cost due to advanced design and materials |
| Flow Characteristics | Typically for on/off applications and allows for small leakage | Low torque requirements, so it is easier to operate |
| Torque Requirements | Generally has a concentric design with the stem centered on the valve body and the disc | Higher torque requirements due to robust sealing |
Selecting the Right Butterfly Valve
High performance butterfly valves offer advanced features and enhanced durability to meet the demands of challenging applications. Whether dealing with high pressures, extreme temperatures, or critical fluid services, these valves provide reliable and efficient flow control across various industries. However, this comes at a higher cost than general service butterfly valves. So, it is necessary to assess operating conditions to know if this extra measure is justified.
At QRC Valves, we have an array of high performance as well as general service butterfly valves for you to choose from. Our knowledgeable team is available to help you select the right valve to ensure optimal performance and longevity.









 .
.