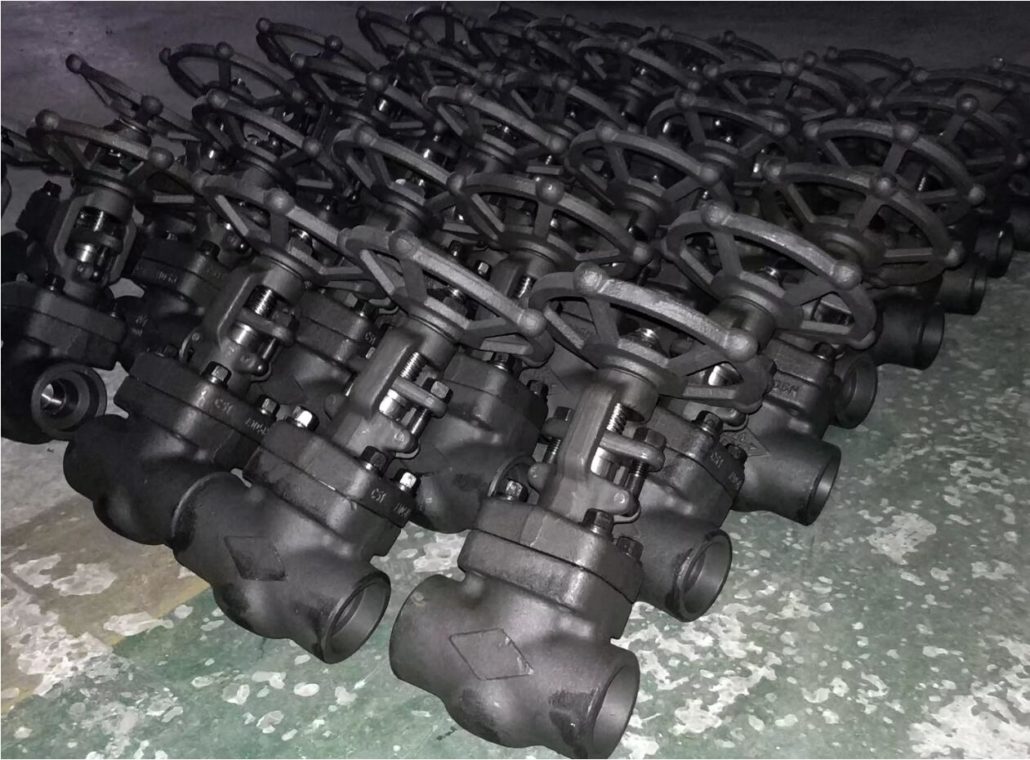
Supapele din oțel forjat sunt mai bune decât supapele din oțel turnat și pot rezista la forțe mari de impact. Plasticitatea, tenacitatea și alte proprietăți mecanice sunt, de asemenea, mai mari decât piesele turnate din oțel, dar diametrul nominal este relativ mic, în general sub DN50. Supapele de turnare au valori de presiune mai mici. Presiunile nominale utilizate în mod obișnuit sunt PN16, PN25, PN40, 150LB-900LB. Clasa de supapă din oțel forjat: PN100, PN160, PN320, 1500LB-3500LB etc. Oțelul turnat este folosit în principal pentru a face piese de formă complexă, dificil de forjat sau tăiat și care necesită rezistență și plasticitate ridicate.
Turnarea este turnare lichidă, iar forjarea este un proces de deformare plastică. Piesa de prelucrat forjată poate îmbunătăți structura internă a structurii, proprietățile mecanice sunt bune, granulele sunt uniforme, iar piesa de prelucrat laborioasă importantă trebuie forjată. Turnarea va provoca segregare structurală, defecte structurale și, desigur, turnarea are avantajele sale. Formarea pieselor complexe de prelucrat nu este ușor de turnat și a fost turnată.
Supapele cu glob din oțel forjat sunt disponibile în trei modele de capotă. Primul tip este un capac de supapă de tip șurub. Corpul supapei proiectat în conformitate cu acest design are un corp de supapă și un capac de supapă conectat prin șuruburi și piulițe și o garnitură de tip bobinat (din grafit flexibil 316 clip). Inelele metalice pot fi folosite și atunci când clienții au cerințe speciale. A doua formă de design este o capotă sudată. Conform acestui design, corpul supapei și capota sunt înșurubate și complet sudate. Toate conexiunile sudate sunt disponibile și atunci când clientul are cerințe speciale. Al treilea tip este un capac de supapă cu auto-strângere de presiune. Supapa proiectată conform acestei forme de proiectare are un corp de supapă și un capac de supapă care sunt înșurubate, iar presiunea internă este etanșată de inelul de etanșare.